3 Personnel T 23 .gif)
3.1 Principle
Personnel, training, experience, awareness
Requirement 1 (see also the quiz)
.jpg)
The right person, in the right place, at the right time
All persons involved in the activities of material reception, production, packaging, inspection, storage and shipping of cosmetic products have appropriate training and experience and are aware of ISO 22716 Good Manufacturing Practices. See also Articles 4, 5 and 25 of the Cosmetic Regulation.
3.2 Organisation
Organization, organization chart
.jpg)
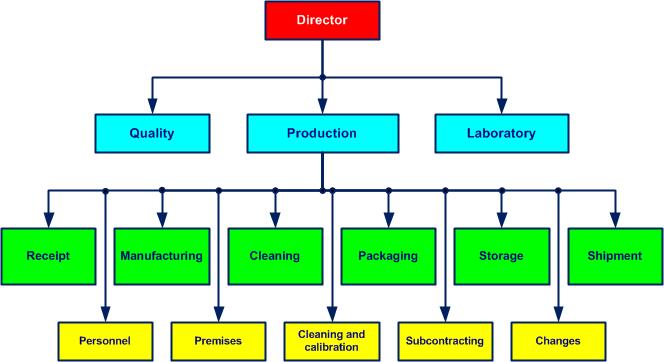
The organizationa structure that satisfies a need (see also ISO 9000, 3.3.1) chart is adapted to the size of the company and the productsany outcome of a process or activity (see also ISO 9000, 3.4.2) manufactured. Top management ensures the availability of the necessary personnel for each activity.
Job descriptions clearly establish the responsibilities and authorities of each position (function, person). Some 30 examples can be found in set D 01.
The independence of each unit (department) is clearly shown in the organizationa structure that satisfies a need (see also ISO 9000, 3.3.1) chart, especially for the quality, production and laboratory departments. The organizationa structure that satisfies a need (see also ISO 9000, 3.3.1)chart is validated by the director. .gif)
3.3 Responsabilités clés
Responsibilities, job descriptions, commitment, participation
.jpg)
Responsibility cannot be shared. Robert Heinlein
The participation and commitment of the staff in the implementation of cosmetic Good Manufacturing Practices is supported by top management (senior executives).
A document identifies the access to the different areas. This document is communicated to all staff. This activity is part of the "Communicate internally and externally" processactivities which transform inputs into outputs (see also ISO 9000, 3.4.1). .jpg)
The organizationa structure that satisfies a need (see also ISO 9000, 3.3.1) chart, job descriptions and other specific documents enable staff to:
- know its place in the structure of the company
- identify its responsibilities, authorities and rights by having access to the necessary documents
- be informed and to follow the requirements of personal hygiene
- report without fear any nonconformity encountered
The "Address risk" processactivities which transform inputs into outputs (see also ISO 9000, 3.4.1) sets out how to identify hazards, assess and deal with risks. .jpg)
Job descriptions identify the responsibilities, authorities and duties of each individual. .gif)
3.4 Formation
Competences, trainings
.jpg)
The personnel have the necessary skills appropriate to the responsibilities and activities carried out on the basis of the training received and the experience gained. Training in good cosmetic manufacturing practices is provided to all personnel. Appropriate training is provided for persons coming into contact with hazardous materials.
A training program is put in place to meet the needs of personnel. Training activities are adapted to the positions, duties and responsibilities and take into account the knowledge and experience of the persons to be trained. An evaluation of the know-how acquired by the personnel is carried out both hot (at the end of the training) and cold (two to three months later). The result of the evaluation of training effectiveness is documented. .gif)
Training is conducted internally, when resources are available, or with the help of external trainers.
The "Provide training" processactivities which transform inputs into outputs (see also ISO 9000, 3.4.1) is a processactivities which transform inputs into outputs (see also ISO 9000, 3.4.1) that is continually being improved. .jpg)
Newly recruited persons receive, in addition to training on cosmetic good manufacturing practices, training on assigned activities. .gif)
Since 2008 (cf. articles L4141-1 to 4 of the French Labour Code) training in terms of safety at the workstation is a legal obligation. The mandatory safety and specific training courses are shown on the INRS site and in the ED 6298 brochure.
Article L6312-1 of the French Labor Code states: “Employee access to continuing professional training is guaranteed:
1° At the initiative of the employer, where appropriate, as part of a training plan;
2° At the employee's initiative, in particular in the context of individual training leave as defined in Article L. 6322-1;
3° At the initiative of the employee with the agreement of his employer within the framework of the individual right to training provided for in Article L. 6323-1 ;
4° As part of the periods of professionalization provided for in Article L. 6324-1;
5° As part of the professionalization contracts provided for in Article L. 6325-1.”
An ISO 22716-certified foundation company relies on a small team of highly versatile technicians in its manufacturing department. These technicians are responsible for a wide range of tasks, including machine operation, minor equipment maintenance, in-process quality checks, and troubleshooting production line issues. Although they are generally qualified, it is difficult to ensure and demonstrate their continued competence in all these diverse tasks, especially when new equipment or processes are introduced.
To answer this question, the quality manager develops a detailed competency matrix for the technician role, breaking down each major task into specific skill and knowledge requirements. A multi-tiered training program is implemented: basic training for all, followed by specialized modules for specific equipment or processes. Technicians are certified for each skill set, and individual competency records are reviewed regularly.
Another approach is to implement a structured cross-training rotation program where technicians regularly rotate between different stations or types of tasks to maintain diverse skills.
3.5 Hygiene
Hygiene, hand washing, appropriate clothing
.jpg)
Hygiene programs are adapted to the context of the company, see annex 12. Hygiene requirementsexplicit or implicit need or expectation (see also ISO 9000, 3.1.2) are fully understood and strictly adhered to by the staff. 
Personnel follow the instructions for using the hand washing facilities to the letter before each entry into a production area. .gif)
Personnel entering the areas of production, inspection and storage of cosmetic products shall wear appropriate and protective clothing to avoid contamination (e.g. uniform, gloves, goggles, hair cover). In these areas it is forbidden (strongly not recommended) to eat, drink, smoke or possess food, beverages, tobacco or medicines. Any unhygienic practices that may deteriorate the productany outcome of a process or activity (see also ISO 9000, 3.4.2) are prohibited.
Persons with apparent illness or with uncovered wounds are excluded from direct contact with cosmetic products. The measures taken to exclude this direct contact are maintained until the medical staff certifies that the danger has been eliminated (the person is in good health).
The personnel manager reviews employee training records. He notes that a new production employee has not been trained in Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP). The employee has not been made aware of basic hygiene rules and does not know how to complete production documents.
The training manager is informed and implements a training plan for all new employees. The training plan includes GMP, hygiene rules, and work instructions.
The quality manager ensures that all employees are trained before being assigned to a position. This reduces product safety risks.
3.6 Visitors
Visitors, restrictions, accompaniment
.jpg)
.gif)
.jpg) Minute of relaxation. Cf. joke "Gold contract".
Minute of relaxation. Cf. joke "Gold contract".- the organization chart shows the independence of the quality department
- the job description of the quality manager includes the task of raising staff awareness of good manufacturing practices
- cold and hot staff evaluations for the training courses provided are up-to-date
- new recruits are informed and have assimilated the induction program
- clothing is always clean (reserve clothing is available)
- the dependency of the production quality department is not defined
- the job description of the quality manager is not up-to-date
- the authority to stop production is not included in the quality manager's job description
- there is no document on staff awareness of good manufacturing practices
- the evaluation of training courses taken is not recorded
- new recruits are not informed about the induction course
- personal hygiene rules are not always followed (dress code not applied for the production area)
