2 Standards, definitions and books
2.1 Standards
Standards and references related to information security

.jpg) The ISO 27000 family includes a large number of standards. Some of the most used standards are shown in figure 2-1:
The ISO 27000 family includes a large number of standards. Some of the most used standards are shown in figure 2-1:
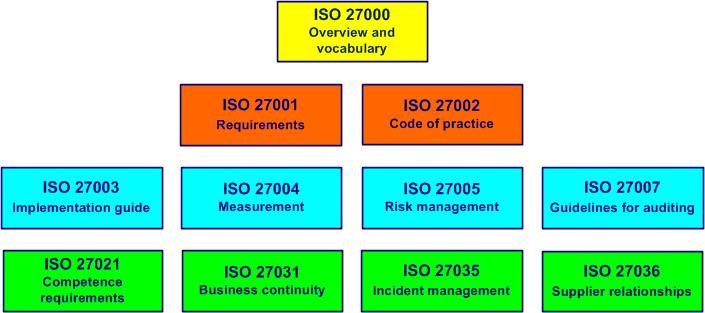
Figure 2-1. ISO 27000 family
- ISO 27000: 2018 - Information technology - Security techniques - Information security management systems (free - PAS - Publicly available specifications) - Overview and vocabulary
- ISO 27001: 2022 - Information security, cybersecurity and privacy protection - Information security management systems - Requirements and comments
- ISO 27002: 2022 - Information security, cybersecurity and privacy protection - Information security controls
- ISO 27003: 2017 - Information technology - Security techniques - Information security management systems - Guidance
- ISO 27004: 2016 - Information technology - Security techniques - Information security management - Monitoring, measurement, analysis and evaluation
- ISO 27005: 2022 - Information security, cybersecurity and privacy protection - Guidance on managing information security risks
- ISO 27007: 2020 - Information security, cybersecurity and privacy protection - Guidelines for information security management systems auditing
- ISO 27008: 2019 - Information technology - Security techniques - Guidelines for the assessment of information security controls
- ISO 27021: 2017 - Information technology - Security techniques - Competence requirements for information security management systems professionals
- ISO 27031: 2011 - Information technology - Security techniques - Guidelines for information and communication technology readiness for business continuity
- ISO 27035-1: 2016 - Information technology - Security techniques - Information security incident management - Part 1: Principles of incident management
- ISO 27035-2: 2016 - Information technology - Security techniques - Information security incident management - Part 2: Guidelines to plan and prepare for incident response
- ISO 27035-3: 2020 - Information technology - Information security incident management - Part 3: Guidelines for ICT incident response operations
- ISO 27036-1: 2021 - Information technology - Security techniques (free - PAS - Publicly available specifications) - Information security for supplier relationships - Part 1: Overview and concepts
- ISO 27036-2: 2014 - Information technology - Security techniques - Information security for supplier relationships - Part 2: Requirements
- ISO 27701: 2019 - Security techniques — Extension to ISO/IEC 27001 and ISO/IEC 27002 for privacy information management — Requirements and guidelines
The standard on auditing is:
ISO 19011 (2018): Guidelines for auditing management systems
The standard ISO 31000: 2018 Risk Management - Guidelines establishes the principles and processactivities which transform inputs into outputs (see also ISO 9000, 3.4.1) for risk management, risk assessment and treatment.
The technical report ISO / TR 31004: 2013 Risk management - Guidelines for the implementation of ISO 31000 provides a better understanding of the principles and organizational framework of risk management.
The standard on business continuity is: ISO 22301 (2019) Security and resilience - Business continuity management systems - Requirements.
Regulation (EU) 2022/2554 of the European Parliament and of the Council of December 14, 2022 on digital operational resilience (DORA - Digital Operational Resilience Act) applicable to EU financial entities from January 17, 2025.
ISO standards (over 21,000) are used in countless fields and are recognized around the world.
Over 28,000 standards (in English and other languages) are available free of charge on the Public.resource.Org site.
2.2 Definitions
Terms and definitions related to information security

The beginning of wisdom is the definitions of terms. Socrates
Some specific terms:
Asset: any element of value to the organization
Availability: property of information to be usable in time (see also ISO 27000, 3.7)
Backup: copy of data in order to archive and protect against loss
Competence: personal skills, knowledge and experiences (see also ISO 9000, 3.10.4)
Confidentiality: property of information accessible only to authorized persons (see also ISO 27000, 3.10)
Conformity: fulfillment of a specified requirement (see also ISO 9000, 3.6.11)
Corrective action: action to eliminate the causes of nonconformity or any other undesirable event and to prevent their recurrence (see also ISO 9000, 3.12.2)
Cryptography: activities of codification and decoding of information
Customer satisfaction: top priority objective of every quality management system related to the satisfaction of customer requirements (see also ISO 9000, 3.9.2)
Customer: anyone who receives a product (see also ISO 9000, 3.2.4)
Effectiveness: capacity to realize planned activities with minimum effort (see also ISO 9000, 3.7.11)
Efficiency: financial relationship between achieved results and resources used (see also ISO 9000, 3.7.10)
Incident (information security): unwanted and unexpected event that can compromise information security (see also ISO 27000, 3.31)
Indicator: value of a parameter, associated with a process objective, allowing the objective measure of its effectiveness (see also FD X50-171, 2.1)
Information security (IS): controls to protect the confidentiality, integrity and availability of information (see also ISO 27000, 3.28)
Information security management system: set of processes allowing the achievement of the information security objectives
Integrity: property of information to be unaltered (see also ISO 27000, 3.36)
Stakeholder: person, group or company that can affect or be affected by an organization (see also ISO 9000, 3.2.3)
IS: information security
ISMS: information security management system
Management system: set of processes allowing objectives to be achieved (see also ISO 9000, 3.5.3)
Nonconformity: non-fulfillment of a specified requirement (see also ISO 9000, 3.6.9)
Objective: measurable goal to be achieved
Organization (company): structure that satisfies a need (see also ISO 9000, 3.2.1)
Process: activities that transform inputs into outputs (see also ISO 9000, 3.4.1)
Product (or service): any outcome of a process or activity (see also ISO 9000, 3.4.2)
Quality: aptitude to fulfill requirements (see also ISO 9000, 3.6.2)
Requirement: explicit or implicit need or expectation (see also ISO 9000, 3.6.4)
Residual risk: risk accepted (see also ISO Guide 73, 3.8.1.6)
Risk assessment: risk identification, analysis and evaluation process (see also ISO Guide 73, 3.4.1)
Risk treatment: risk reduction activities (see also ISO Guide 73, 3.8.1)
Risk: likelihood of occurrence of a threat or an opportunity (see also ISO Guide 73, 1.1)
Statement of applicability (SoA): document describing the objectives and security controls
Supplier (external provider): an entity that provides a product (see also ISO 9000, 3.2.5)
Top management: group or persons in charge of the organizational control at the highest level (see also ISO 9000, 3.1.1)
Traceability: aptitude to memorize or restore all or part of a trace of executed functions (see also ISO 9000, 3.6.13)
VLAN : Virtual Local Area Network
Vulnerability: weakness of an asset that could lead to unauthorized access (see also ISO 27000, 3.77)
In the terminology of management systems, do not confuse:
- accident and incident
- an accident is an unexpected serious event
- an incident is an event that can lead to an accident
- anomaly, defect, dysfunction, failure, nonconformity, reject and waste:
- an anomaly is a deviation from what is expected
- a defect is the non-fulfillment of a requirement related to an intended use
- a dysfunction is a degraded function that can lead to a failure
- a failure is when a function has become unfit
- a nonconformity is the non-fulfillment of a requirement in production
- a reject is a nonconforming product that will be destroyed
- a waste is when there are added costs but no value
- audit program and plan
- an audit program is the annual planning of the audits
- an audit plan is the description of the audit activities
- audit, inspection, auditee and auditor
- an audit is the process of obtaining audit evidence
- an inspection is the conformity verification of a process or product
- an auditee is the one who is audited
- an auditor is the one who conducts the audit
- control and optimize
- control is meeting the objectives
- optimize is searching for the best possible results
- customer, external provider and subcontractor
- a customer receives a product
- an external provider provides a product on which specific work is done
- a subcontractor provides a service or product on which specific work is done
- effectiveness and efficiency
- effectiveness is the level of achievement of planned results
- efficiency is the ratio between results and resources
- follow-up and review
- follow-up is the verification of the obtained results of an action
- review is the analysis of the effectiveness in achieving objectives
- inform and communicate
- to inform is to give someone meaningful data
- to communicate is to pass on a message, to listen to the reaction and discuss
- objective and indicator
- an objective is a sought after commitment
- an indicator is the information on the difference between the pre-set objective and the achieved result
- organization and enterprise, society, company
- organization is the term used by the ISO 9001 standard as the entity between the supplier and the customer
- an enterprise, society and company are examples of organizations
- process, procedure, product, activity and task
- a process is how we satisfy the customer using people to achieve the objectives
- a procedure is the description of how we should conform to the rules
- a product is the result of a process
- an activity is a set of tasks
- a task is a sequence of simple operations
- safety and security
- safety is prevention against malicious risks
- security is prevention against risks of unintentional origin
Information is stored in multiple ways such as:
- digital (data stored electronically)
- physical (on paper or other)
- knowledge (the know-how of the staff)
Information is transmitted in different ways such as:
- digital (electronic mail)
- physically (post)
- verbally (meetings)
Remark 1: the use of ISO 27000 and ISO 9000 definitions is recommended. The most important thing is to determine a common and unequivocal vocabulary for everyone in the company.
Remark 2: the customer can also be the user, the beneficiary, the trigger, the ordering party or the consumer.
Remark 3: documented information is any information that we must maintain (procedure  ) or retain (record
) or retain (record  ).
).
Remark 4: an asset is a broad concept. An asset can be:
- information
- a document
- an archive
- infrastructure
- technical equipment
- software
- the staff
- the reputation of the organization
- a process
- a service
For other definitions, comments, explanations and interpretations that you do not find in this module and annex 06 you can consult: .jpg)

- ISO online consultation platform (OBP)
- IEC Electropedia
2.3 Books
Books related to information security

When I think of all the books still left for me to read, I am certain of further happiness. Jules Renard
.jpg) Books for further reading on quality and information security:
Books for further reading on quality and information security:
.jpg) Edwards Deming, Out of the Crisis, MIT Press, 1982
Edwards Deming, Out of the Crisis, MIT Press, 1982(1).jpg) Eliyahu Goldratt, Jeff Cox, The Goal, A Process of Ongoing Improvement, North River Press, 1984
Eliyahu Goldratt, Jeff Cox, The Goal, A Process of Ongoing Improvement, North River Press, 1984.jpg) Masaaki Imai, KAIZEN, The Key to Japan’s Competitive Success, McGraw-Hill, 1986
Masaaki Imai, KAIZEN, The Key to Japan’s Competitive Success, McGraw-Hill, 1986 Edward Humphreys, Implementing the ISO/IEC 27001 2013 ISMS Standard, Artech House, 2016
Edward Humphreys, Implementing the ISO/IEC 27001 2013 ISMS Standard, Artech House, 2016 Douglas Landoll, Information security policies, procedures, and standards, Auerbach Publications, 2016
Douglas Landoll, Information security policies, procedures, and standards, Auerbach Publications, 2016 Dejan Kosutic, Secure & simple, A small-business guide to implementing iso 27001 on your own, Advisera Expert Solutions, 2016
Dejan Kosutic, Secure & simple, A small-business guide to implementing iso 27001 on your own, Advisera Expert Solutions, 2016 Dejan Kosutic, ISO 27001 Risk management in plain english, step-by-step handbook for information security practitioners in small businesses, Advisera Expert Solutions, 2016
Dejan Kosutic, ISO 27001 Risk management in plain english, step-by-step handbook for information security practitioners in small businesses, Advisera Expert Solutions, 2016 Dejan Kosutic, ISO 27001 annex A controls in plain english, Step-by-step handbook for information security practitioners in small businesses, Advisera Expert Solutions, 2016
Dejan Kosutic, ISO 27001 annex A controls in plain english, Step-by-step handbook for information security practitioners in small businesses, Advisera Expert Solutions, 2016 Raphaël Hertzog et al, Kali Linux Revealed: Mastering the Penetration Testing Distribution, OFFSEC Press, 2017
Raphaël Hertzog et al, Kali Linux Revealed: Mastering the Penetration Testing Distribution, OFFSEC Press, 2017 Cees van der Wens, ISO 27001 handbook: Implementing and auditing an 'Information Security Management System' in small and medium-sized businesses, Brave New Books, 2020
Cees van der Wens, ISO 27001 handbook: Implementing and auditing an 'Information Security Management System' in small and medium-sized businesses, Brave New Books, 2020 Abhishek Chopra, Mukund Chaudary, Implementing an Information Security Management System, Apress, 2020
Abhishek Chopra, Mukund Chaudary, Implementing an Information Security Management System, Apress, 2020 Deepak D. Kalambkar, Implementing ISO 27001 Simplified: Full Fledged Information on Implementing End-to-End Information Security with Real Time Statistical Data and Analysis, Notion Press, 2021
Deepak D. Kalambkar, Implementing ISO 27001 Simplified: Full Fledged Information on Implementing End-to-End Information Security with Real Time Statistical Data and Analysis, Notion Press, 2021 Cesare Gallotti, Information security - 2022 Edition. Risk management. Management systems. The ISO/IEC 27001:2022 standard. The ISO/IEC 27002:2022 controls, Youcanprint, 2022
Cesare Gallotti, Information security - 2022 Edition. Risk management. Management systems. The ISO/IEC 27001:2022 standard. The ISO/IEC 27002:2022 controls, Youcanprint, 2022 David Brewer, An introduction to ISO/IEC 27001:2022, Independently published, 2022
David Brewer, An introduction to ISO/IEC 27001:2022, Independently published, 2022 Hasan YILDIZ, ISO 27001: Practical Guide to Implementing ISO 27001 Information Security Management, Independently published, 2023
Hasan YILDIZ, ISO 27001: Practical Guide to Implementing ISO 27001 Information Security Management, Independently published, 2023 Mohamed Atef, Mastering ISO 27001: 2022: Your Comprehensive Guide to Implementing the Latest ISO 27001 Standard with Real-World Use Cases, Examples, and Templates, Independently published, 2023
Mohamed Atef, Mastering ISO 27001: 2022: Your Comprehensive Guide to Implementing the Latest ISO 27001 Standard with Real-World Use Cases, Examples, and Templates, Independently published, 2023 Erik Rorstorm, ISO 27001 Foundation - Study Guide: A Comprehensive Study Guide for ISO 27001 Foundation Certification (English Edition), Kindle, 2023
Erik Rorstorm, ISO 27001 Foundation - Study Guide: A Comprehensive Study Guide for ISO 27001 Foundation Certification (English Edition), Kindle, 2023
.jpg) Minute of relaxation. Game: Procedure
Minute of relaxation. Game: Procedure
