2 Standards, definitions and books
2.1 Standards
Standards and references

The main standards related to the prevention of bribery are:.jpg)
- ISO 26000 (2010): Guidance on social responsibility
- ISO 9000 (2015): Quality management systems — Fundamentals and vocabulary
- ISO 9001 (2015): Quality management systems — Requirements
- ISO 37001 (2016): Anti-bribery management systems — Requirements with guidance for use
- ISO 31000 (2018): Risk management — Guidelines
- ISO 19011 (2018): Guidelines for auditing management systems
- IEC 31010 (2019): Risk management — Risk assessment techniques
- ISO/IEC 17000 (2020): Conformity assessment — Vocabulary and general principles
- ISO 37301 (2021): Compliance management systems — Requirements with guidance for use
- ISO 37002 (2021): Whistleblowing management systems — Guidelines
None of these standards are mandatory, but as Deming said:
It is not necessary to change. Survival is not mandatory
2.2 Definitions
Terms and definitions related to bribery and management systems

The beginning of wisdom is the definition of terms. Socrates
The verb to corrupt comes from the Latin corrumpere: to break completely, to deteriorate, physically or morally.
There are many definitions of the word corruption (bribery). Some examples:
- a form of dishonesty or a criminal offense which is undertaken by a person or an organization which is entrusted in a position of authority, in order to acquire illicit benefits or abuse power for one's personal gain. Wikipedia
- abuse of delegated power for private purposes. Transparency International
- the use and abuse of public power for private gain. Council of Europe
- offering, promising, giving, accepting or soliciting of an undue advantage of any value (which could be financial or non-financial), directly or indirectly, and irrespective of location(s), in violation of applicable law, as an inducement or reward for a person acting or refraining from acting in relation to the performance of that person’s duties. ISO 37001 (2016)
- abuse of public office for personal gain. World Bank
- characterized by improper conduct (such as bribery or the selling of favors). Merriam-Webster dictionary
Our preference:
Bribery: abuse of power for personal gain
In order not to confuse hazard and risk, some simple examples are shown in table 2-1:
Table 2-1
| Hazard | Risk |
| slippery ground | broken leg |
| electricity | electrocution |
| tobacco | lung cancer |
| climb a ladder | to break an arm falling |
As shown in 2-1 the time of exposure to hazard multiplies the risk:

Figure 2-1. Hazard exposure
Risk (and its level) is a function of impact and likelihood (figure 2-2).

Figure 2-2. Risk level
The risk is residual when the impact and likelihood are low, cf. figure 2-3. As soon as the impact and likelihood are high, we approach the critical zone (red).

Figure 2-3. Risk criticality
More details on the risk levels are shown in annex 02.
Some definitions and acronyms related to bribery, risk and the management system:
ABMS: anti-bribery management system
Active bribery: the corruptor's proposal of an unfair advantage
Anti-bribery management system (ABMS): set of processes to reduce bribery
Benchmarking: comparative analysis method in connection with one or more competitors
Brainstorming: team approach to developing ideas and finding solutions
Bribe (bakchich): payment to a civil servant so that he acts more favorably
Bribery risk management: refers to the aspects of the policies and practices of an institution (public or private) which define, make it possible to assess and aim to mitigate the internal and external risks of corruption present in the context of its activities (OECD)
Business risk management: global approach to controlling uncertainties and their interactions in business
Cf.: confer (from Latin), compare, see
Control: see inspection
Customer: the person who receives a product
Due diligence: assessment of the risk of bribery and actions to reduce this risk
Fraud: falsification of data, invoices and other administrative documents
Grand corruption: high and very high level corruption (policy makers)
Hazard: situation that could lead to an incident
Identify the hazard: ask yourself what could go wrong
Impact: consequence of an event affecting the objectives
Inspection: the actions of measuring, testing and examining a process, product or material to establish whether requirements are met
Likelihood: possibility that something happens
Management system: set of processes allowing objectives to be achieved
Misappropriation of funds: theft of public resources by an official
MS: management system
Nonconformity: non-fulfillment of a specified requirement
Non-quality: gap between expected quality and perceived quality
Opportunity: uncertain event that could have a favorable impact
Organization (company): structure that satisfies a need
Passive bribery: the acceptance of the corrupted of an unfair advantage
Petty bribery: bribery in public administration
Quality: aptitude to fulfill requirements
Requirement: implicit or explicit need or expectation
Responsibility: capacity to make a decision alone
Risk analysis: activity to understand the nature of a risk and determine its impact
Risk assessment: process for identifying, analyzing and evaluating risk
Risk factor (peril, danger): element likely to cause a risk
Risk identification: assessment activity to find and describe risks
Risk level: criticality of the risk according to the impact and likelihood
Risk management plan: risk management planning including approach, steps, methods, resources
Risk management: activities to restrict the possibility that something goes wrong
Risk manager: person with the responsibility and authority to manage risk
Risk prevention: activities based on decreasing risk likelihood of occurrence
Risk protection: activities based on reducing risk impacts
Risk severity: measurement of risk impact
Risk threshold: acceptance limit (below) or non-tolerance limit (above)
Risk treatment: risk modification activities
Risk: likelihood of occurrence of a threat or an opportunity
Safety: absence of unacceptable risk
Strategy: total approach to achieve objectives
System: set of interactive processes
Threat: uncertain event that could have a negative impact on the objectives
Uncertainty: existence of more than one possibilit
In the terminology of management systems, do not confuse:
- accident and incident
- an accident is an unexpected serious event
- an incident is an event that can lead to an accident
- anomaly, defect, dysfunction, failure, nonconformity, reject and waste:
- anomaly is a deviation from what is expected
- defect is the non-fulfillment of a requirement related to an intended use
- dysfunction is a degraded function that can lead to a failure
- failure is when a function has become unfit
- nonconformity is the non-fulfillment of a requirement in production
- reject is a nonconforming product that will be destroyed
- waste is when there are added costs but no value
- audit program and plan
- an audit program is the annual planning of the audits
- an audit plan is the description of the audit activities
- audit, inspection, auditee and auditor
- an audit is the process of obtaining audit evidence
- an inspection is the conformity verification of a process and product
- an auditee is the one who is audited
- an auditor is the one who conducts the audit
- control and optimize
- control is meeting the objectives
- optimize is searching for the best possible results
- customer, external provider and subcontractor
- a customer receives a product
- an external provider provides a service or a product
- a subcontractor provides a product or service on which specific work is done
- effectiveness and efficiency
- effectiveness is the level of achievement of planned results
- efficiency is the ratio between results and resources
- follow-up and review
- follow-up is the verification of the obtained results of an action
- review is the analysis of the effectiveness in achieving objectives
- hazard, problem and risk
- hazard is the state, the situation, the source which can lead to an accident
- the problem is the gap between the actual situation and the desired situation
- risk is the measure, the consequence of a hazard and it is always a potential problem
- inform and communicate
- to inform is to give someone meaningful data
- to communicate is to pass on a message, to listen to the reaction and discuss
- mapping and organization chart
- mapping is the graphical presentation of processes and their interactions in a company
- the organizational chart is the graphic presentation of the departments and their links in a company
- objective and indicator
- an objective is a sought after commitment
- an indicator is the information on the difference between the pre-set objective and the achieved result
- organization and enterprise, society, company
- organization is the term used by the ISO 9001 standard as the entity between the supplier and the customer
- an enterprise, society and company are examples of organizations
- prevention and protection, cf. figure 2-4
- prevention is the means to reduce the likelihood and frequency of occurrence of a risk (check tire pressure)
- protection is the means to limit the impact of a risk (fasten your seat belt)
- probability, uncertainty and likelihood
- the probability expresses the quantitative analysis of the uncertainty
- uncertainty is the inaccuracy of predicting
- the likelihood expresses the qualitative analysis of the uncertainty
- process, procedure, product, activity and task
- a process is how we satisfy the customer using people to achieve the objectives
- a procedure is the description of how we should conform to the rules
- a product is the result of a process
- an activity is a set of tasks
- a task is a sequence of simple operations
- safety and security
- safety is prevention against malicious risks
- security is prevention against risks of unintentional origin
Figure 2-4 Prevention and protection
Remark 1: between stakeholders and interested parties our preference is for stakeholders
Remark 2: between impact, gravity, consequence and severity our preference is for impact
Remark 3: between anti-bribery manager and anti-corruption compliance or anti-corruption officer our preference is for anti-bribery manager
Remark 4: between likelihood and probability our preference is for likelihood (of occurrence)
Remark 5: a risk can have negative impacts (we speak of threats) or positive impacts (we speak of opportunities), cf. ISO 21500, 4.3.28. Seizing an opportunity is taking risks, but not seizing an opportunity can put us at risk. Often risk is equated with hazard (danger) and commonly used instead of threat
Remark 6: each time you use the expression "opportunity for improvement" instead of nonconformity, malfunction or failure, you will gain a little more trust from your interlocutor (external or internal customer)
For other definitions, comments, explanations and interpretations that you cannot find in this module and annex 06, you can consult:.jpg)
- ISO Online Browsing platform (OBP)
- IEC Electropedia
The icons used in the module:
.jpg) explanation, example, detail, rule
explanation, example, detail, rule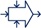 process
process.gif) procedure (documented)
procedure (documented).gif) record
record joke
joke game
game trap to avoid
trap to avoid
2.3 Books
Books related to bribery and corruption

When I think of all the books still left for me to read, I'm certain of further happiness. Jules Renard
To go further, some books, listed in chronological order:.jpg)
 Eoin O'Shea, The Bribery Act 2010: A Practical Guide, Jordan Publishing, 2011
Eoin O'Shea, The Bribery Act 2010: A Practical Guide, Jordan Publishing, 2011-
 Leslie Holmes, Corruption: A Very Short Introduction, OUP Oxford, 2015
Leslie Holmes, Corruption: A Very Short Introduction, OUP Oxford, 2015  Monty Raphael, Bribery: Law and practice, Oxford University Press, 2016
Monty Raphael, Bribery: Law and practice, Oxford University Press, 2016 Alan Field, ISO 37001: An Introduction to Anti-Bribery Management Systems, ITGP, 2017
Alan Field, ISO 37001: An Introduction to Anti-Bribery Management Systems, ITGP, 2017 Joe Khamisi , The Bribery Syndrome: How Multinational Corporations Collude with Dictators to Raid Africa's Natural Resources, Jodey Book Publishers, 2019
Joe Khamisi , The Bribery Syndrome: How Multinational Corporations Collude with Dictators to Raid Africa's Natural Resources, Jodey Book Publishers, 2019 Team, ISO 37001 A Complete Guide - 2021 Edition, The Art of Service, 2020
Team, ISO 37001 A Complete Guide - 2021 Edition, The Art of Service, 2020  Régis Bismouth et al, The Transnationalization of Anticorruption Law, Routledge, 2021
Régis Bismouth et al, The Transnationalization of Anticorruption Law, Routledge, 2021 Team, Compliance ISO 37001 A Complete Guide - 2021 Edition
Team, Compliance ISO 37001 A Complete Guide - 2021 Edition Shaomin Li, Bribery and Corruption in Weak Institutional Environments, Cambridge University Press, 2022
Shaomin Li, Bribery and Corruption in Weak Institutional Environments, Cambridge University Press, 2022 Alexei Maksurov, Bribery: Investigative and qualification issues, Our Knowledge Publishing, 2023
Alexei Maksurov, Bribery: Investigative and qualification issues, Our Knowledge Publishing, 2023 Robert W. McGee at al, The Ethics of Bribery: Theoretical and Empirical Studies, Springer International Publishing, 2023
Robert W. McGee at al, The Ethics of Bribery: Theoretical and Empirical Studies, Springer International Publishing, 2023
Some sites, rich in documents on the prevention of bribery:
- the hundred UN guides: unglobalcompact.org/library
- dozens of documents from the NGO: Transparency International
- the guides, charters, studies and others of the French Anti-Corruption Agency
- numerous documents from the International Chamber of Commerce
- the wide variety of documents on corruption from the Partnership Against Corruption Initiative (PACI)
And free online training from the UN: https://thefightagainstcorruption.org/:
“This e-learning tool is a joint product of the UN Global Compact and the UN Office on Drugs and Crime. It uses six interactive learning modules to further the audience's understanding of the UN Global Compact's 10th principle against corruption and the UN Convention against Corruption as it applies to the private sector. The tool is targeted at everyone who acts on behalf of a company. Each module only lasts about five minutes, providing a quick and effective way of learning. And it is fun too!”
