2 Definitions, standards and books
2.1 Definitions
Definitions, acronyms
The beginning of wisdom is the definition of terms. Socrates
A risk can have negative impacts (we speak of threats) or positive impacts (we speak of opportunities).
Seizing an opportunity is taking risks, but not seizing an opportunity can expose us to risk.
Often risk is assimilated with hazard or danger and commonly used instead of threat.
There are multiple definitions of the word risk. Some examples:
- the likelihood that something will happen. IFRIMA (1994)
- combination of the probability of the occurrence of a dangerous event and the severity of the injury or harm to health caused to people by this event. ILO-OSH (2001)
- combination of the probability of an event and its consequences. ISO Guide 73 (2002)
- the possibility that something will happen that will impact the objectives. AS 4360 (2004)
- uncertainty of outcomes, whether a positive opportunity or a negative threat. OGC - UK (2005)
- effect of uncertainty on objectives. ISO Guide 73 (2009)
- description of a specific event that may or may not occur, as well as its causes and consequences. IRM (2013)
- effect of uncertainty. ISO 45001 (2018)
- combination of the probability of occurrence of harm and the severity of that harm. ISO 14971 (2019)
- the risk should be proportional to the probability of occurrence as well as the extent of damage. Blaise Pascal
- possible hazard, more or less predictable. Little Robert
- negative effect of uncertainty. Christopher Paris
- mathematical expectation of an event probability function. Daniel Bernoulli
- event whose random occurrence is likely to cause damage to people or property or both at the same time. Serge Braudo
- the extent of the potential loss. Evan Picoult
- the future impact of an uncontrolled danger. Sean Chamberlin
- the extent of the danger. Georges-Yves Kervern
- probability and magnitude of a loss, disaster or other adverse event. Douglas Hubbard
Our preference:
Risk: likelihood of occurrence of a threat or an opportunity
Some definitions of risk management:
- coordinated activities to direct and control an organization with regard to risk. ISO Guide 73 (2009)
- systematic application of management policies, procedures and practices to analysis, evaluation, control and risk management tasks. ISO/IEC 63 (2019)
- culture, processes and structures in place to effectively manage opportunities and negative impacts. Business Continuity Institute
- be smart to take risks. Douglas Hubbard
- provides a framework for organizations to control and respond to uncertainties. Paul Hopkins
- the act or practice of risk. Edmund Conrow
Our preference:
Risk management: activities to restrict the possibility that something goes wrong
Some definitions of the word hazard (or hazardous situation):
- source or situation likely to cause trauma and pathologies. ISO 45001 (2018)
- source of potential harm. ISO/IEC Guide 63 (2019)
- what constitutes a threat, a risk for someone, something. Larousse
- what threatens or compromises the safety or existence of a person or thing. Little Robert
- intrinsic property of a substance, of a system which can lead to damage. Yvan Vérot
Our preference:
Hazard: situation that could lead to an incident
Identify the hazard: ask yourself what could go wrong
Some definitions of risk evaluation:
- overall process of risk identification, risk analysis and risk evaluation. ISO Guide 73 (2009)
- overall process comprising a risk analysis and a risk evaluation. ISO/IEC Guide 51 (2014)
- assessment of undesirable outcomes and assigning probabilities to their chances of occurrence. Vlasta Molak
- qualitative and quantitative risk assessment process and determination of the type of analysis to be carried out. Quebec Office of the French Language
Our preference:
Risk evaluation: process of risk identification, analysis and evaluation
Some definitions of risk identification:
- process of finding, recognizing and describing risks. ISO Guide 73 (2009)
- process for reviewing program areas and each critical technical process to identify and document associated risk. Edmund Conrow
Our preference:
Risk identification: assessment activity to find and describe risks
Some definitions of risk analysis:
- process to comprehend the nature of risk and to determine the level of risk. ISO Guide 73 (2009)
- systematic use of available information to identify hazards and to estimate the risk. ISO Guide 63 (2019)
- process of examining each identified risk issue or process to refine the description of the risk, isolate the cause and determine the effects. Edmund Conrow
- systematic use of information to identify sources and assign risk values. Terje Aven
Our preference:
Risk analysis: activity to understand the nature of a risk and determine its impact
Some definitions of risk treatment:
- process of developing, selecting and implementing controls. BS 31100 (2011)
- process to modify risk. ISO Guide 73 (2009)
- process that identifies, evaluates, selects and implements options to set risk at acceptable levels given the constraints and objectives of the program. Edmund Conrow
Our preference:
Risk treatment: risk modification activities
Some definitions of the word opportunity:
- positive effect of uncertainty. Christopher Paris
- potential for achieving desired and positive outcomes of an event. Robert Charrette
Our preference:
Opportunity: uncertain event that may have a favorable impact
Uncertainty and probability (likelihood) are subjective notions with invented quantities.
Impact: consequence of an event affecting the objectives
Likelihood: possibility that something happens
Probability can be considered as a measure of uncertainty. If probability can be measured it is therefore linked to something that has happened. Likelihood is a more general notion because it can include an effect that never happened.
To avoid confusing hazard and risk, a few simple examples:
| Hazard | Risk |
| slippery floor | broken leg |
| electricity | electrocution |
| tobacco | lung cancer |
| climb a ladder | break your arm when falling |
Risk depends on its context. Example:
- driving a car in town involves a minimal risk of accident
- driving a car in the city, but in a country in civil war, can lead to irreparable harm
As shown in figure 2-1, the time of exposure to hazard multiplies the risk:

Figure 2-1. Exposure to hazard
Risk (and its level) is a function of impact and likelihood of occurrence (figure 2-2).

Figure 2-2. The level of risk
The risk is residual when the impact and likelihood of occurrence are low, cf. figure 2-3. As soon as the impact and likelihood are high, we approach the critical zone (red).
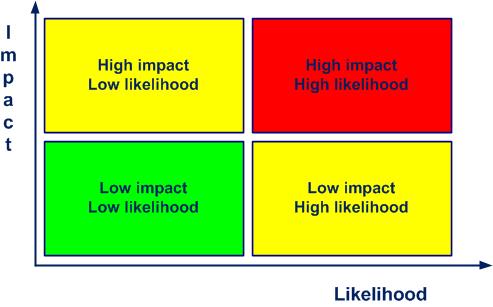
Figure 2-3. The criticality of the risk
More details on risk levels are shown in annex 02. 
Some definitions and acronyms:
Attitude towards risk: evaluating and treating risk
Benchmarking: comparative analysis technique against one or more competitors
Brainstorming: method allowing the development of ideas from the participants in order to find solutions
Business continuity management: method aimed at ensuring that in the event of a crisis, critical functions remain operational or become operational again as quickly as possible (see also resilience)
Business continuity plan: business continuity management planning including approach, steps, methods, resources
Conformity: fulfillment of a specified requirement
Control plan: document describing the specific measures to carry out the control of a product or process
Control: see inspection
Corrective action: action to eliminate the causes of nonconformity or any other undesirable event and to prevent their recurrence
Criticality: level of a potential risk
Customer: anyone who receives a product
Effectiveness: capacity to perform planned activities with minimum effort
Efficiency: financial relationship between achieved results and resources used
Harm: bodily injury or damage to human health, property or the environment
Inspection: actions of measuring, testing and reviewing a product, service, process or material to determine compliance with requirements
ISO: international organization for standardization
Kaizen: from Japanese, kai = change and zen = good (for the better, better), Kaizen = continual improvement
Level of risk: criticality of the risk based on impact and likelihood
Life cycle: all phases in the life of a product from design to disposal
Management system: set of processes allowing objectives to be achieved
Manager: someone who gets results through other people
Manufacturer: person or group responsible for the design, manufacturing, packaging and labeling of a good
MCT: multiple choice test
Medical device (MD): product or service used for the purposes of diagnosis, prevention, monitoring, treatment, mitigation of disease or injury
Monitoring: set of planned actions to guarantee the effectiveness of control measures
MS: management system
Nonconformity (NC): non-fulfillment of a specified requirement
Non-quality: gap between expected and perceived quality
Organization: structure that satisfies a need
Preventive action: action to eliminate the potential causes of nonconformity or any other undesirable event and to prevent their appearance
Problem: gap that must be reduced to obtain a result
Process: activities that transform input into output
Product (or service): any result of a process or activity
QM: quality manager
Requirement: implicit or explicit need or expectation
Residual risk: acceptable risk following the implementation of risk control measures
Resilience: ability to resolve a crisis and continue operating as before
Responsibility: capacity to make a decision alone
Risk control: risk reduction activities
Risk criteria: indices to evaluate the importance of risk
Risk factor (peril, danger): element likely to cause a risk
Risk management plan: risk management planning including approach, steps, methods, resources
Risk management system: set of processes enabling risk objectives to be achieved
Risk measure: set of possibilities with quantified probabilities and losses
Risk owner: person with responsibility and authority to control risk
Risk prevention: activities to reduce the likelihood of risk occurrence
Risk protection: activities to reduce risk impacts
Risk register: folder containing information relating to identified risks
Risk severity: measuring the impact of risk
Risk threshold: acceptance limit (below) or non-tolerance limit (above)
RMS: risk management system
Safety: lack of unacceptable risk
Stakeholder: person, group or company that can affect or be affected by an organization
Strategy: total approach to achieve objectives
Supplier: entity that provides a product
System: set of interacting processes
Threat: uncertain event that could have a negative impact on the objectives
Top management (direction): group or persons responsible for management at the highest level of the company
Uncertainty: existence of more than one possibility
Waste: anything that adds cost but not value
In the terminology of management systems, do not confuse:
- accident and incident
- an accident is an unexpected serious event
- an incident is an event that can lead to an accident
- anomaly, defect, dysfunction, failure, nonconformity, reject and waste:
- an anomaly is a deviation from what is expected
- a defect is the non-fulfillment of a requirement related to an intended use
- a dysfunction is a degraded function that can lead to a failure
- a failure is when a function has become unfit
- a nonconformity is the non-fulfillment of a requirement in production
- a reject is a nonconforming product that will be destroyed
- a waste is when there are added costs but no value
- audit program and plan
- an audit program is the annual planning of the audits
- an audit plan is the description of the audit activities
- audit, inspection, auditee and auditor
- an audit is the process of obtaining audit evidence
- an inspection is the conformity verification of a process or product
- an auditee is the one who is audited
- an auditor is the one who conducts the audit
- control and optimize
- to control is to meet the objectives
- to optimize is to search for the best possible results
- customer, external provider and subcontractor
- a customer receives a product
- an external provider provides a product on which specific work is done
- a subcontractor provides a service or product on which specific work is done
- effectiveness and efficiency
- effectiveness is the level of achievement of planned results
- efficiency is the ratio between results and resources
- follow-up and review
- follow-up is the verification of the obtained results of an action
- review is the analysis of the effectiveness in achieving objectives
- hazard, problem and risk
- hazard is the state, the situation or the source that can lead to an accident
- problem is the gap between the actual situation and the desired situation
- risk is the measure, the consequence of a hazard and it is always a potential problem
- inform and communicate
- to inform is to give someone meaningful data
- to communicate is to pass on a message, to listen to the reaction and discuss
- objective and indicator
- an objective is a sought-after commitment
- an indicator is the information on the difference between the pre-set objective and the achieved result
- organization and enterprise, society, company
- organization is the term used by the ISO 9001 standard as the entity between the supplier and the customer
- an enterprise, society and company are examples of organizations
- prevention and protection, cf. figure 2-4
- prevention is the means to reduce the likelihood and frequency of occurrence of a risk (checking tire pressure)
- protection is the means to limit the impact of a risk (fastening your seat belt)
- process, procedure, product, activity and task
- a process is how we satisfy the customer using people to achieve the objectives
- a procedure is the description of how we should conform to the rules
- a product is the result of a process
- an activity is a set of tasks
- a task is a sequence of simple operations
- risk and crisis management
- risk management is like fire prevention
- crisis management is like putting out a fire
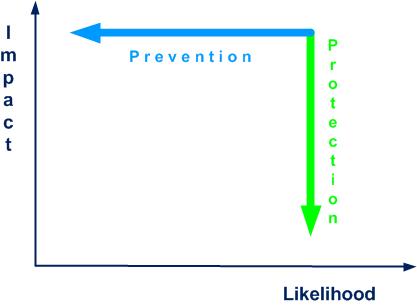
Figure 2-4. Prevention and protection
Remark 1: the most important thing is to determine a common and unequivocal vocabulary for everyone in the company.
Remark 2: between likelihood and probability our preference is for likelihood.
Remark 3: the customer can also be the user, the beneficiary, the trigger, the ordering party or the consumer.
Remark 4: each time you use the expression "opportunity for improvement" instead of nonconformity, malfunction or failure, you will gain a little more trust from your interlocutor (external or internal customer).
For other definitions, comments, explanations and interpretations that you don’t find in this module and in annex 06, you can consult: 

- ISO Online Browsing Platform (OBP)
- IEC Electropedia
.jpg) Minute of relaxation. Game: Procedure
Minute of relaxation. Game: Procedure
2.2 Standards
Standards related to risks

Risk-related standards (in chronological order):
- AS 4360 (1995): Risk management
- IRM/Alarm/AIRMIC (2002): A Risk Management Standard (Risk Management Reference Framework)
- FD X50-117 (2003): Project management - Risk management - Project risk management
- IEC 60601-1 (2005): Medical electrical equipment - Part 1: General requirements for basic safety and essential performance
- FD X50-252 (2006): Risk management - Guidelines for risk estimation
- IEC 62304 (2006): Medical device software - Software life cycle processes
- BS 31100 (2008): Risk management - code of practice
- 768/2008/CE: Uniform conditions for the marketing of safe products in the EU (conformity marking)
- ISO Guide 73 (2009): Risk management - Vocabulary
- FD X50-253 (2011): Risk management - Risk management process - Guidelines for communication
- BP Z74-700 (2011): Business Continuity Plan (BCP)
- NF S99-170 (2013): Maintenance of medical devices - Quality management system for the maintenance of medical devices and the management of risks associated with their use
- FD ISO 31004 (2014): Risk management - Guidelines for the implementation of ISO 31000
- FD X50-259 (2014): Risk management - Business continuity plan (PCA) - Implementation and maintenance approach
- IEC 62366-1 (2015): Medical devices - Part 1: Application of usability engineering to medical devices
- ISO 13485 (2016): Medical devices - Quality management systems - Requirements for regulatory purposes
- FD X50-260 (2016): Risk management - Guidelines for implementation in ETI/SMEs and other organizations - ETI/SME-PMI
- 2017/745 (2017): Regulation (EU) 2017/745 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 5 April 2017 on medical devices
- NF S99-172 (2017): Use and maintenance of medical devices - Risk management system for risks associated with the use of medical devices
- ISO 31000 (2018): Risk management – Guidelines
- ISO 10993-1 (2018): Biological evaluation of medical devices - Part 1: Evaluation and testing within a risk management process
- NF EN ISO 14971 (2019): Medical devices - Application of risk management to medical devices
- IEC 31010 (2019): Risk management - Risk assessment techniques
- ISO Guide 63 (2019): Guide to the development and inclusion of aspects of safety in International Standards for medical devices
- ISO 20916 (2019): In vitro diagnostic medical devices - Clinical performance studies using specimens from human subjects - Good study practice
- ISO/TR 24971 (2020): Medical devices - Guidance on the application of ISO 14971
- ISO/TR 20416 (2020): Medical devices - Post-market surveillance for manufacturers
- XP S99-223 (2020): Medical Device - Benefit risk management
- ISO 14155 (2020): Clinical investigation of medical devices for human subjects - Good clinical practice
- BS 31100 (2021): Risk management. Code of practice
- ISO 20417 (2021): Medical devices - Information to be supplied by the manufacturer
- ISO 10017 (2021): Quality management - Guidance on statistical techniques for ISO 9001:2015
Two French documents related to the processes with explanations, recommendations and examples:
- AC X50-178 (agreement, 2002) Quality management – Process management – Good practices and feedback
- FD X50-176 (documentation booklet, 2017) Management tools – Process management
Risk management – ENA – 2020 bibliography.
None of these standards are obligatory but as Deming said:
There is no need to change. Survival is not obligatory
2.3 Books
Books related to risks and MDs

When I think of all the books still left for me to read, I am certain of further happiness. Jules Renard
To go further, some books, classified in chronological order:
 Frank Knight, Risk, Uncertainty And Profit, University of Chicago Press, 1921
Frank Knight, Risk, Uncertainty And Profit, University of Chicago Press, 1921 Peter Bernstein, Against the Gods: The Remarkable Story of Risk, John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1998
Peter Bernstein, Against the Gods: The Remarkable Story of Risk, John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1998 Michael Gallagher, Business Continuity Management - How to Protect Your Company from Danger, Prentice Hall, 2002
Michael Gallagher, Business Continuity Management - How to Protect Your Company from Danger, Prentice Hall, 2002 Edmund Conrow, Effective Risk Management: Some Keys to Success, AIAA, 2003
Edmund Conrow, Effective Risk Management: Some Keys to Success, AIAA, 2003 Tom Kendrick, Identifying and managing project risk: Essential Tools for Failure-Proofing Your Project, AMACOM, 2003
Tom Kendrick, Identifying and managing project risk: Essential Tools for Failure-Proofing Your Project, AMACOM, 2003 Nancy Tague, The Quality Toolbox, ASQC Quality Press, 2005
Nancy Tague, The Quality Toolbox, ASQC Quality Press, 2005 Mark Abkowitz, Operational risk management, Wiley, 2008
Mark Abkowitz, Operational risk management, Wiley, 2008 Dennis Dickstein, No excuses, A business process approach to managing operational risk, Wiley, 2009
Dennis Dickstein, No excuses, A business process approach to managing operational risk, Wiley, 2009 team, Management of Risk: Guidance for Practitioners, Stationery Office Books, 2010
team, Management of Risk: Guidance for Practitioners, Stationery Office Books, 2010 Torben Andersen, Strategic Risk Management Practice: How to Deal Effectively with Major Corporate Exposures, Cambridge University Press, 2010
Torben Andersen, Strategic Risk Management Practice: How to Deal Effectively with Major Corporate Exposures, Cambridge University Press, 2010  Antonio Borghesi, Barbara Gaudenzi, Risk Management, How to Assess, Transfer and Communicate Critical Risks, Springer, 2013
Antonio Borghesi, Barbara Gaudenzi, Risk Management, How to Assess, Transfer and Communicate Critical Risks, Springer, 2013 Eric Myhrberg, A Practical Field Guide for Iso 13485 2003, ASQ, 2013
Eric Myhrberg, A Practical Field Guide for Iso 13485 2003, ASQ, 2013 Karl Weick, Kathleen Sutcliffe, Managing the Unexpected: Sustained Performance in a Complex World, Wiley, 2015
Karl Weick, Kathleen Sutcliffe, Managing the Unexpected: Sustained Performance in a Complex World, Wiley, 2015 ISO 31000 - Risk Management - A practical guide for SMEs, ISO, 2015
ISO 31000 - Risk Management - A practical guide for SMEs, ISO, 2015 Risk, Issue, and Opportunity Management Guide for Defense Acquisition Programs, Deputy Assistant Secretary of Defense Systems Engineering, 2017
Risk, Issue, and Opportunity Management Guide for Defense Acquisition Programs, Deputy Assistant Secretary of Defense Systems Engineering, 2017  COSO, Enterprise Risk Management - Integrating with Strategy and Performance, AICPA, 2017
COSO, Enterprise Risk Management - Integrating with Strategy and Performance, AICPA, 2017 Greg Hutchins, ISO 31000: 2018 Enterprise Risk Management, Certified Enterprise Risk Manager (R) Academy, 2018
Greg Hutchins, ISO 31000: 2018 Enterprise Risk Management, Certified Enterprise Risk Manager (R) Academy, 2018 AICPA, Practice Aid: Enterprise Risk Management: Guidance For Practical Implementation and Assessment, 2018, Wiley, 2018
AICPA, Practice Aid: Enterprise Risk Management: Guidance For Practical Implementation and Assessment, 2018, Wiley, 2018 Dyadem, Guidelines for Failure Mode and Effects Analysis for Medical Devices, CRC Press, 2018
Dyadem, Guidelines for Failure Mode and Effects Analysis for Medical Devices, CRC Press, 2018 James Kline, Enterprise Risk Management in Government: Implementing ISO 31000:2018, Quality Plus Engineering, 2019
James Kline, Enterprise Risk Management in Government: Implementing ISO 31000:2018, Quality Plus Engineering, 2019 ISO 31000 Risk Management A Complete Guide - 2021 Edition, The Art of Service, 2020
ISO 31000 Risk Management A Complete Guide - 2021 Edition, The Art of Service, 2020 Amir Samimi, A Review of Risk Management According to ISO 31000, 2018, Scholars' Press, 2020
Amir Samimi, A Review of Risk Management According to ISO 31000, 2018, Scholars' Press, 2020 Douglas W. Hubbard, The Failure of Risk Management: Why It's Broken and How to Fix It 2nd Edition, Wiley, 2020
Douglas W. Hubbard, The Failure of Risk Management: Why It's Broken and How to Fix It 2nd Edition, Wiley, 2020 Gerardus Blokdyk, ISO 14971 A Complete Guide - 2021 Edition, 5STARCooks, 2020
Gerardus Blokdyk, ISO 14971 A Complete Guide - 2021 Edition, 5STARCooks, 2020 Gerardus Blokdyk, ISO 13485 A Complete Guide - 2020 Edition, 5STARCooks, 2020
Gerardus Blokdyk, ISO 13485 A Complete Guide - 2020 Edition, 5STARCooks, 2020  Bijan Elahi, Safety Risk Management for Medical Devices, Academic Press, 2021
Bijan Elahi, Safety Risk Management for Medical Devices, Academic Press, 2021 Fundamentals of Risk Management: Understanding, Evaluating and Implementing Effective Enterprise Risk Management 6th Edition, Kogan Page, 2021
Fundamentals of Risk Management: Understanding, Evaluating and Implementing Effective Enterprise Risk Management 6th Edition, Kogan Page, 2021 Jennifer Geary, How to be a Chief Risk Officer: A handbook for the modern CRO, Neilsen, 2022
Jennifer Geary, How to be a Chief Risk Officer: A handbook for the modern CRO, Neilsen, 2022
None of these books are mandatory...
