2 Definitions, standards and books
2.1 Definitions
Definitions, abreviations, terminology

The beginning of wisdom is the definition of terms. Socrates
A risk can have negative impacts (we speak of threats) or positive impacts (we speak of opportunities).
Seizing an opportunity is taking risks, but not seizing an opportunity can expose us to risk.
There are multiple definitions of the word risk. Some examples:
- combination of the probability of occurrence of damage and its severity. ISO 51 (1999)
- combination of the probability of an event and its consequences. ISO Guide 73 (2002)
- combination of the probability of the occurrence of a dangerous event and the severity of the injury or harm to health caused to people by this event. ILO-OSH (2001)
- possible danger more or less predictable. Little Robert
- description of a specific event that may or may not occur, as well as its causes and consequences. MRI (2013)
- effect of uncertainty on the achievement of objectives. ISO Guide 73 (2009)
- effect of uncertainty on objectives. ISO 22301 (2019)
- effect of uncertainty. ISO 45001 (2018)
- negative effect of uncertainty. Christopher Paris
- mathematical expectation of an event probability function. Daniel Bernoulli
- event whose random occurrence is likely to cause damage to people or property or both at the same time. Serge Braudo
- uncertain possible event whose occurrence does not depend exclusively on the will of the parties and which could cause damage. Larousse
- uncertainty of outcomes, whether a positive opportunity or a negative threat. OGC - UK (2005)
- the future impact of an uncontrolled danger. Sean Chamberlin
- the extent of the danger. Georges-Yves Kervern
- the possibility that something will happen that will impact the objectives. AS 4360 (2004)
- the likelihood that something will happen. IFRIMA (1994)
- the extent of the potential loss. Evan Picoult
- the risk should be proportional to the probability of occurrence as well as the extent of damage. Blaise Pascal
- probability and magnitude of a loss, disaster or other adverse event. Douglas Hubbard
Our preference:
Risk: likelihood of occurrence of a threat or opportunity
Identifying hazards means asking yourself what could go wrong
Often risk is equated with danger and commonly used instead of threat.
Uncertainty and probability are subjective notions with fictitious quantities.
Probability can be considered as a measure of uncertainty. If probability can be measured it is therefore linked to something that has happened. Likelihood is a more general notion because it can include an effect that never happened.
Some definitions and abbreviations:
Activity: set of tasks to obtain a deliverable
BCP: business continuity plan
Benchmarking: comparative analysis method in connection with one or more competitors Business impact analysis (BIA): analysis of the impact of a disruption on the business
Brainstorming: method allowing the development of ideas from the participants in order to find solutions
Business continuity management system (BCMS): set of processes enabling business continuity objectives to be achieved
Business continuity management: method aimed at ensuring that in the event of a crisis, critical functions remain operational or become operational again as quickly as possible (see also resilience)
Business continuity manager: leader to the resilience journey
Business continuity: ability of a company to continue delivering products and providing services during and after a disruption
Conformity: fulfillment of a specified requirement
Corrective action: action to eliminate the causes of nonconformity or any other undesirable event and to prevent their recurrence
Customer: anyone who receives a product
Disruption: incident which results in deviation from the delivery of products and the provision of services
Effectiveness: capacity to realize planned activities with minimum effort
Efficiency: financial relationship between achieved results and used resources
Fail safe device: system allowing the prevention of errors by eliminating the human factor
FMEA: Failure Mode and Effects Analysis
Hazard: situation that could lead to an incident
Impact: consequence of an event affecting the objectives
Kaizen: from Japanese kai - change, zen - better. Continual improvement step by step to create more value and less waste. Approach based on common sense and staff awareness
Likelihood: possibility that something happens
Management system (MS): set of processes allowing objectives to be achieved
Monitoring: pack of planned actions to guarantee the effectiveness of the critical control points
MTPD: maximum tolerable period of disruption
Non-quality: gap between expected quality and perceived quality
Opportunity: uncertain event that could have a favorable impact
Requirement: explicit or implicit need or expectation
Resilience: ability to resolve a crisis and continue to function as before
Responsibility: capacity to make a decision alone
Risk analysis: methodical analysis of the existence of a hazard to understand its nature and to facilitate the adoption of control measures
Risk assessment: risk identification, analysis and evaluation process
Risk criteria: indices to assess the importance of the risk
Risk estimation: activities to assign values to the likelihood and impact of risk
Risk evaluation: risk assessment activities to determine whether the risk is acceptable
Risk factor (peril, danger): element likely to cause a risk
Risk identification: risk assessment activity to find and describe risks
Risk level: criticality of the risk according to the impact and likelihood
Risk management plan: risk management planning including approach, steps, methods, resources
Risk management system: set of processes allowing the achievement of the risk objectives
Risk management: activities to restrict the possibility that something goes wrong
Risk measurement: set of possibilities with quantified probabilities and losses
Risk owner: person with responsibility and authority to manage risk
Risk prevention: activities based on decreasing risk likelihood of occurrence
Risk protection: activities based on reducing risk impacts
Risk register: folder containing information relating to identified risks
Risk severity: measuring the impact of the risk
Risk threshold: acceptance (below) or non-tolerance (above) limit
Risk treatment: risk reduction activities
Security: ability to avoid an unwanted event
Strategy: total approach to achieve objectives
SWOT: Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats. Tool for structuring a risk analysis
System: set of interacting processes
Threat: uncertain event that could have a negative impact on the objectives
Uncertainty: existence of more than one possibility
Waste: anything that adds cost but no value
In the terminology of management systems do not confuse:
- accident and incident
- an accident is an unexpected serious event
- an incident is an event that can lead to an accident
- anomaly, defect, dysfunction, failure, nonconformity, reject and waste:
- anomaly is a deviation from what is expected
- defect is the non-fulfillment of a requirement related to an intended use
- dysfunction is a degraded function that can lead to a failure
- failure is when a function has become unfit
- nonconformity is the non-fulfillment of a requirement in production
- reject is a nonconforming product that will be destroyed
- waste is when there are added costs but no value
- audit program and plan
- an audit program is the annual planning of the audits
- an audit plan is the description of the audit activities
- audit, inspection, auditee and auditor
- an audit is the process of obtaining audit evidence
- an inspection is the conformity verification of a process and product
- an auditee is the one who is audited
- an auditor is the one who conducts the audit
- control and optimize
- control is meeting the objectives
- optimize is searching for the best possible results
- customer, external provider and subcontractor
- a customer receives a product
- an external provider provides a service or a product
- a subcontractor provides a product or service on which specific work is done
- effectiveness and efficiency
- effectiveness is the level of achievement of planned results
- efficiency is the ratio between results and resources
- follow-up and review
- follow-up is the verification of the obtained results of an action
- review is the analysis of the effectiveness in achieving objectives
- hazard, problem and risk
- hazard is the state, the situation, the source which can lead to an accident
- the problem is the gap between the actual situation and the desired situation
- risk is the measure, the consequence of a hazard and it is always a potential problem
- inform and communicate
- to inform is to give someone meaningful data
- to communicate is to pass on a message, to listen to the reaction and discuss
- mapping and organization chart
- mapping is the graphical presentation of processes and their interactions in a company
- the organizational chart is the graphic presentation of the departments and their links in a company
- objective and indicator
- an objective is a sought after commitment
- an indicator is the information on the difference between the pre-set objective and the achieved result
- organization and enterprise, society, company
- organization is the term used by the ISO 9001 standard as the entity between the supplier and the customer
- an enterprise, society and company are examples of organizations
- prevention and protection, cf. figure 2-1
- prevention is the means to reduce the likelihood and frequency of occurrence of a risk (check tire pressure)
- protection is the means to limit the impact of a risk (fasten your seat belt)
- probability, uncertainty and likelihood
- the probability expresses the quantitative analysis of the uncertainty
- uncertainty is the inaccuracy of predicting
- the likelihood expresses the qualitative analysis of the uncertainty
- process, procedure, product, activity and task
- a process is how we satisfy the customer using people to achieve the objectives
- a procedure is the description of how we should conform to the rules
- a product is the result of a process
- an activity is a set of tasks
- a task is a sequence of simple operations
- safety and security
- safety is prevention against malicious risks
- security is prevention against risks of unintentional origin
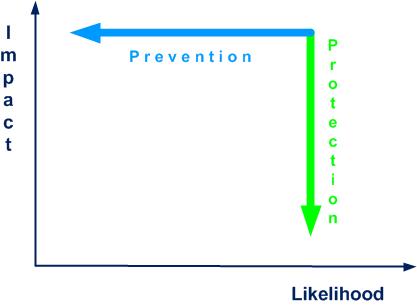
Figure 2-1 Prevention and protection
For other definitions, comments, explanations and interpretations that you cannot find in this module and annex 06, you can consult: .jpg)
.gif)
- ISO Online Browsing platform (OBP)
- IEC Electropedia
Remark 1: between stakeholders and interested parties our preference is for stakeholders
Remark 2: between impact, gravity, consequence and severity our preference is for impact
Remark 3: between likelihood and probability our preference is for likelihood (of occurrence)
Remark 4: each time you use the expression "opportunity for improvement" instead of nonconformity, malfunction or failure, you will gain a little more trust from your interlocutor (external or internal customer)
The icons used in the module:
.jpg) explanation, example, detail, rule
explanation, example, detail, rule- process
.gif) procedure (documented)
procedure (documented).gif) record
record joke
joke game
game trap to avoid
trap to avoid
2.2 Standards
Standards, history

There can be no improvements where there are no standards. Masaaki Imai
Standards and specifications related to risks and business continuity (in chronological order):
- AS 4360 (1995), Risk Management
- ANAO Better Practice Guide (2000), Business Continuity Management—Keeping the wheels in motion
- BSI PAS 56 (2003), Guide to Business Continuity Management
- HB 221 (2004), Business Continuity Management
- NFPA 1600 (2004), Standard on Disaster/Emergency Management and Business Continuity Programs
- BS 25999-1 (2006), Business Continuity Management – Part 1: Code of Practice
- FD X50-252 (2006), Management du risque - Lignes directrices pour l'estimation des risques (Risk Management - Guidelines for Risk Estimation)
- BS 25999 – 2 (2007), Business Continuity Management – Specification
- ISO/PAS 22399 (2007), Societal Security - Guideline for Incident Peparedness and Operational Continuity Management
- SI 24001 (2007) Organizational Resilience Management System (ORMS) – Requirements and Guidance for Use
- ISO Guide 73 (2009), Risk Management - Vocabulary
- ANSI/ASIS SPC1 (2009), Organisational Resilience: Security, Preparedness, and Continuity Management Systems – Requirements with Guidance for Use
- SS 540 (2008), Singapore Standard for Business Continuity Management (BCM)
- ANSI/ASIS/BSI BCM.01 (2010), Business Continuity Management Systems: Requirements with Guidance for Use
- BP Z74-700 (2011), Repository of Best Practises - Business Continuiy Plan (BCP)
- ISO/IEC 27031 (2011), Information Technology - Security Techniques - Guidelines for Information and Communication Technology Readiness for Business Continuity
- ISO 22398 (2013), Societal Security, Guidelines for Exercises
- FD X50-259 (2014), Risk Management - Business Continuity Plan - Implementation and Maintenance Procedure
- BS 11200 (2014), Crisis Management - Guidance and Good Practice
- BS 65000 (2014), Guidance on Organizational Resilience
- ISO 22316 (2017), Security and Resilience - Organizational Resilience - Principles and Attributes
- ISO 31000 (2018), Risk Management - Guidelines
- ISO 19011 (2018), Guidelines for Auditing Management Systems
- ISO/TS 22330 (2018), Security and Resilience - Business Continuity Management Systems - Guidelines for People Aspects of Business Continuity
- ISO/TS 22331 (2018), Security and Resilience - Business Continuity Management Systems - Guidelines for Business Continuity Strategy
- ISO 22320 (2018), Security and resilience, Emergency management, Guidelines for Incident Management
- ISO 22301 (2019), Security and Resilience - Business Continuity Management Systems - Requirements
- IEC 31010 (2019), Risk Management - Risk Assessment Techniques
- ISO 22313 (2020), Security and Resilience - Business Continuity Management Systems - Guidance on the use of ISO 22301
- AS/NZS 5050(Int) (2020), Managing Disruption-Related Risk
- BS 31100 (2021), Risk Management. Code of Practice
- ISO 22300 (2021), Security and Resilience - Vocabulary
- ISO/TS 22317 (2021), Security and Resilience - Business Continuity Management Systems - Guidelines for Business Impact Analysis
- ISO/TS 22318 (2021), Security and Resilience - Business Continuity Management Systems - Guidelines for Supply Chain Continuity Management
- ISO 22322 (2022) Security and Resilience, Emergency Management, Guidelines for Public Warning
- ISO/IEC 27001 (2022), Information Security, Cybersecurity and Privacy Protection - Information Security Management Systems - Requirements
None of these standards are obligatory but as Deming said:
There is no need to change. Survival is not mandatory
2.3 Books
Books related to risk and continuity management 
.jpg) To go further, some books, classified in chronological order:
To go further, some books, classified in chronological order:
-
 Frank Knight, Risk, Uncertainty And Profit, University of Chicago Press, 1921
Frank Knight, Risk, Uncertainty And Profit, University of Chicago Press, 1921 -
.jpg) Edwards Deming, Out of the Crisis, MIT Press, 1982
Edwards Deming, Out of the Crisis, MIT Press, 1982 -
 Peter Bernstein, Against the Gods: The Remarkable Story of Risk, John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1998
Peter Bernstein, Against the Gods: The Remarkable Story of Risk, John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1998 -
 Michael Gallagher, Business Continuity Management - How to Protect Your Company from Danger, Prentice Hall, 2002
Michael Gallagher, Business Continuity Management - How to Protect Your Company from Danger, Prentice Hall, 2002 -
 Nancy Tague, The Quality Toolbox, ASQC Quality Press, 2005
Nancy Tague, The Quality Toolbox, ASQC Quality Press, 2005 -
 Douglas Hubbard, The Failure of Risk Management: Why It's Broken and How to Fix It, Wiley, 2009
Douglas Hubbard, The Failure of Risk Management: Why It's Broken and How to Fix It, Wiley, 2009 -
 team, Business Continuity For Dummies, For Dummies, 2012
team, Business Continuity For Dummies, For Dummies, 2012 -
 Susan Snedaker, Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery Planning for IT Professionals, Syngress, 2013
Susan Snedaker, Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery Planning for IT Professionals, Syngress, 2013 -
 team, ISO 22301 A Complete Guide - 2021 Edition, The Art of Service, 2020
team, ISO 22301 A Complete Guide - 2021 Edition, The Art of Service, 2020 -
 Alan Carder, ISO 22301:2019 and business continuity management - Understand how to plan, implement and enhance a business continuity management system (BCMS), IT GP, 2021
Alan Carder, ISO 22301:2019 and business continuity management - Understand how to plan, implement and enhance a business continuity management system (BCMS), IT GP, 2021 -
 PECB, ISO 22301:2019 Auditing Guide: A simple and practical guide to auditing a Business Continuity Management System (BCMS), PECB, 2021
PECB, ISO 22301:2019 Auditing Guide: A simple and practical guide to auditing a Business Continuity Management System (BCMS), PECB, 2021 -
 Kris Hermans, Mastering ISO 22301:2019: A Comprehensive Guide to the Business Continuity Management System (BCMS), Independently published, 2023
Kris Hermans, Mastering ISO 22301:2019: A Comprehensive Guide to the Business Continuity Management System (BCMS), Independently published, 2023 -
 Arman Suman, ISO 22301 Foundation - Study Guide, Kindle, 2023
Arman Suman, ISO 22301 Foundation - Study Guide, Kindle, 2023 -
 James Crask, Business Continuity Management: A Practical Guide to Organization Resilience and ISO 22301, KoganPage, 2024
James Crask, Business Continuity Management: A Practical Guide to Organization Resilience and ISO 22301, KoganPage, 2024
.jpg) Minute of relaxation. Game: Procedure
Minute of relaxation. Game: Procedure
When I think of all the books still left for me to read, I am certain of further happiness. Jules Renard
